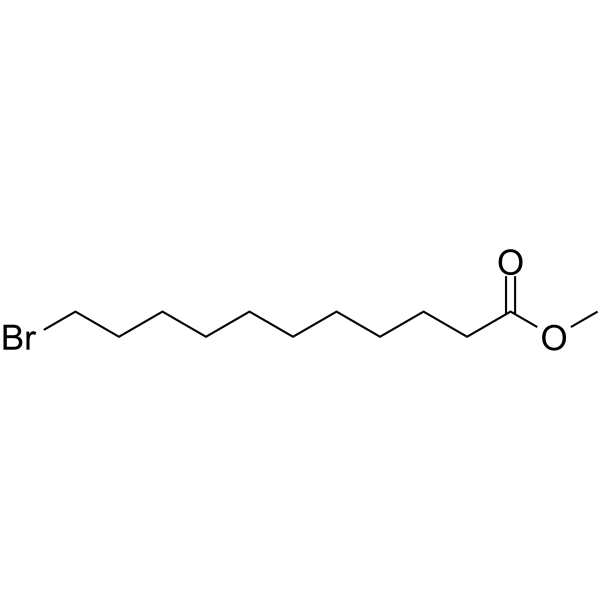
Br-C10-methyl ester
CAS No. 6287-90-7
Br-C10-methyl ester( —— )
Catalog No. M26930 CAS No. 6287-90-7
Br-C10-methyl ester is a PROTAC linker, which refers to the alkyl/ether composition. Br-C10-methyl ester is used in the synthesis of a series of PROTACs (MS432).
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 500MG | 50 | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameBr-C10-methyl ester
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionBr-C10-methyl ester is a PROTAC linker, which refers to the alkyl/ether composition. Br-C10-methyl ester is used in the synthesis of a series of PROTACs (MS432).
-
DescriptionBr-C10-methyl ester is a PROTAC linker, which refers to the alkyl/ether composition. Br-C10-methyl ester is used in the synthesis of a series of PROTACs (MS432).
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorJNK| MMP-9| p38
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number6287-90-7
-
Formula Weight279.218
-
Molecular FormulaC12H23BrO2
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 100 mg/mL (358.15 mM)
-
SMILESCOC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCBr
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Lucidenic acids-rich extract from antlered form of Ganoderma lucidum enhances TNFα± induction in THP-1 monocytic cells possibly via its modulation of MAP kinases p38 and JNK.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Apr 29;408(1):18-24.
molnova catalog



related products
-
[Nle13]-Motillin
[Nle13]-Motillin
-
Cyclosporin A-Deriva...
Cyclosporin A-Derivative 1 is a crystalline intermediate derived from the opening of cyclosporin A extracted from patent WO 2013167703 A1.
-
DAPI Dihydrochloride
DAPI Dihydrochloride is a cell-permeable fluorescent probe by binding in the minor grove of A-T rich sequences of DNA, used to stain DNA and chromosomes, with a preference for adenine and thymine rich DNA.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


